According to Lou Faulkner Williams, which aspects of Reconstruction elicited most resistance from white southerners? In which aspects do you think opponents of Reconstruction had their best and worst arguments?
Week 6: Reconstruction
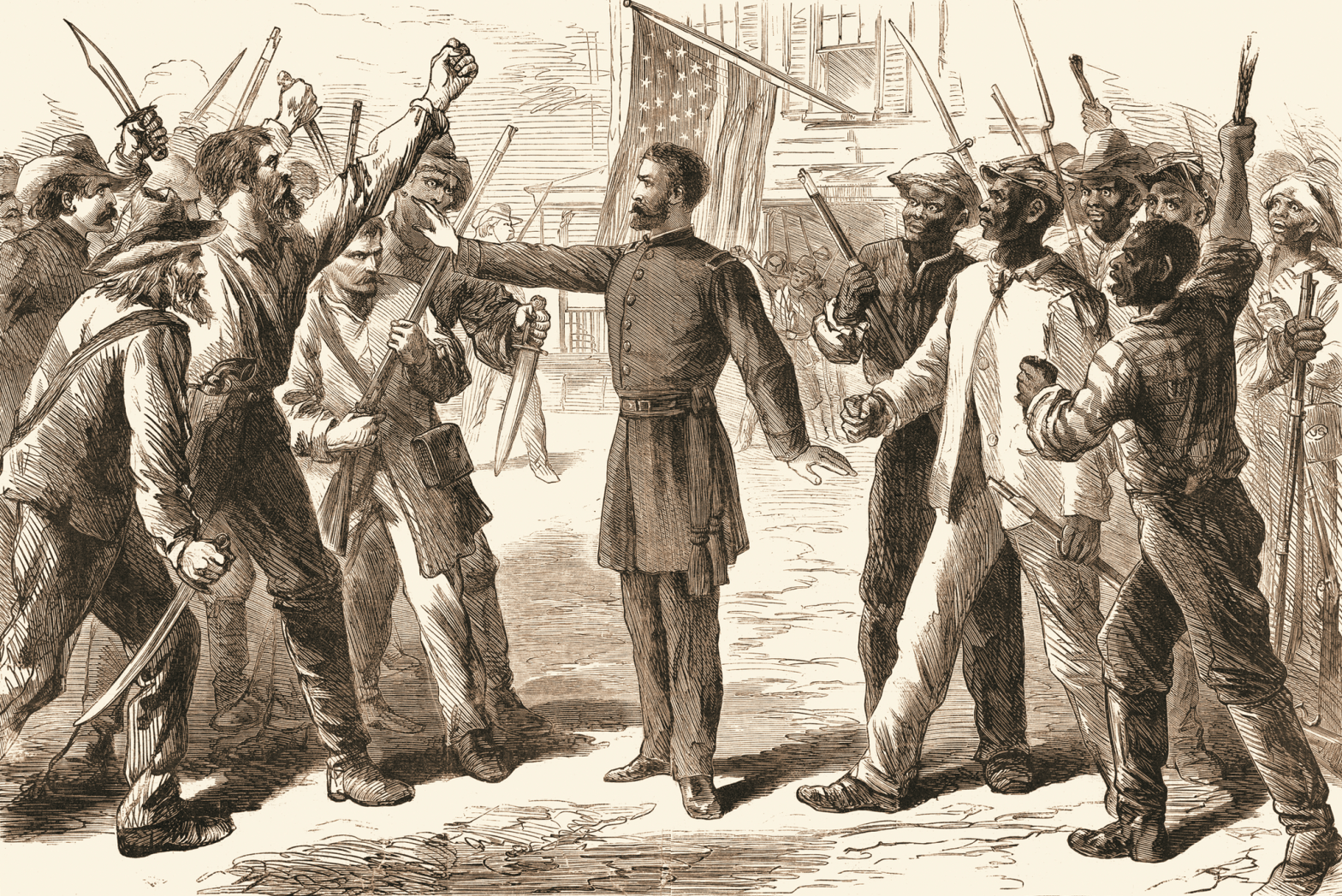
According to Lou Faulkner Williams, which aspects of Reconstruction elicited most resistance from white southerners? In which aspects do you think opponents of Reconstruction had their best and worst arguments?
The opponents of Reconstruction, white Southerners, were adamant over their southern values in relation to growing federal encroachment over changing political and social structures. White Southerners were especially resistant to freedmen’s desire for political access and legitimization of their citizenship and humanity. Black freedmen, understandably, wanted to be seen as equal men and citizens to white men. They wanted their citizenship legitimized, by having the same equal rights, including right to trial of jury, as white men. White Southerners refused to be part of the political process if it constituted equality to freedmen. Many of them boycotted the polls. White South Carolinian’s saw the Republican’s push for democracy, land redistribution, and equal services to freedmen as a violation of their equal rights because their loyalty to laissez-faire principles argued for neutral policies.
White Southerners always had a deeply rooted fear over slave insurrections and the changes that would occur after emancipation. They were worried that there was going to be a race war and thus, it was important to keep newly freed slaves into the same oppressive system to prevent the worsening of economic and social changes they endured after the Civil War. I think this argument held by opponents is the most compelling because it shows how embedded racial inequality is that this reasoning still continues to flourish within white supremacy groups today. White supremacists still believe that there will be a race war and white people must remain vigilant against others so they can ascertain their traditional Southern values. Opponents of removing Confederate statues in the South argue that it is a removal of Southern values and history but ignores what exactly those values and history entails. Moreover, the argument that black people are better off as slaves so they can be better protected by their slaveholders as property is not considerate to what “better off” means. Domestic slaves were more likely to leave, even though they were arguably more endeared upon than field laborers, which shows that no matter how protective slaveholders were, many people did not want to remain under that care. As freedmen, people may have experienced brutal difficulties but they also endured that while being slaves.
LikeLike
Excellent, Gleo – thanks.
LikeLike
White southerners resisted any aspects of Reconstruction in which they were expected to allow newly freed black citizens to enjoy their rights, especially if the white southerners felt it threatened their dominance in society. They wished to maintain as similar a system to the one they had with slavery as possible. The Black Code of 1865 forced black people to stay in agricultural and servant jobs and stay dependent on their white employers. An aspect that the white southerners resisted a lot was freedmen and Republican northerners taking their spots in the government when the white southerners refused to or were unable to vote. They called the government fraud and believed that they were being oppressed since they were being taxed without proper representation. They also believed that the Republicans were promoting the interests of freedmen over the interests of the white Democrats. They resisted letting black people vote and the Ku Klux Klan used violence to keep them away from the polls.
The aspect that had their best argument was that the South Carolina government was promoting one group’s interests over another which violated laissez-faire constitutional neutrality. Many of the representatives in the government were trying to use high taxes to free up land owned by white South Carolinians so that freedmen could own land and establish their own farms. This was promoting the interests of one group over another. Their worst argument was that black people needed to depend on white people because they were not self sufficient. They limited their rights with the Black Code of 1865 arguing that it was for their own protection, but in reality the southern freedmens’ biggest threat was white southerners and the Ku Klux Klan, which was made up of white southerners. They were being forced to depend on their biggest threat.
LikeLike
The all-encompassing issue here was the fact that, as Williams said, “sharing rights with freedmen was unthinkable.” It didn’t seem that any aspect of this change elicited a good response – almost all of it was negative. The issues here were political and social equality for the freedman – the idea of a former slave having more power or “power over” their white counterparts. From William’s writing, what seemed to piss White southerners off the most was the deprivation of their voices. The fact that the government moved to take from them to give to their former slaves was incomprehensible. As Williams mentioned, they saw the “redistributive measures of the government as ‘confiscation’.”
LikeLike
The creation of new state constitutions that promoted black suffrage and the ratification of the 14th amendment to be readmitted to the union elicited the most resistance from white southerners. White southerners were either prohibited from voting in the constitutional convention or decided to protest it and thus, they lost representation in the new state government and constitution. Due to this, white South Carolinians did not see the legitimacy in the new state government which saw a republican majority and “carpetbaggers” in state offices. This saw most resistance because white southerners responded to an “unauthorized” state government by supporting or being complicit in Klan terrorism. Former slave-owning white southerners had the worst argument as opponents of reconstruction. They were more concerned with protecting their class interests and felt as if the redistributive legislation favored the freedmen more instead of the laissez-faire system which they were used to. Instead of focusing on the economic and financial strains that arose from the civil war, former white slave owners were only concerned with preserving their class interests.
LikeLike
Amongst all of the reforms that were instituted during the post-Civil War period of Reconstruction, slavery, without a doubt, elicited the most resistance from white Southerners. The abolishment of slavery not only challenged their “nationalistic goals” (Faulkner 2) and their pro-white ideologies, but their economic well-being as well.
To begin with the latter, Faulkner notes that, “The enormous… economic hardships caused by war in South Carolina hardened racial attitudes among the whites and diminished whatever paternalism had endeared the slaves to their masters and protected them from other whites” (2–3). On the surface, it is easy to comprehend that any business or trade that makes use of slave labor is bound to be profitable (even lucrative if the circumstances permit). The South’s economic exigency to plant, harvest, and sell valuable cash crops such as cotton and tobacco compelled slave owners to suspend their moral dispositions in favor of adopting a slave work force to complete the manual labor. Whether or not slavery would have been an economically bountiful practice in the long term, the abolishment of slavery did in fact thrust the South into economic turmoil. To reiterate Faulker’s point, this financial despondency only fueled Southern tensions, particularly toward black citizens and the Union.
This brewing abhorrence toward Union ideals and legislation incited an undermining of the newly established law of the land by white Southerners. As Faulkner explains, “[In South Carolina,] night riders terrorized black citizens almost nightly over a period of several months in 1870 and 1871, forcing the freedmen to sleep in the woods and swaps for fear of their lives” (2). Other negative responses to the Reconstruction included the rise of the Ku Klux Klan and the Black Code of 1865. While, from a constitutional perspective, it was possible for white Southerners to claim that the abolishment of slavery was an action not protected by the Constitution (given that slaves constituted as “private property”), their claim to keeping slavery in tact was completely shredded at the moral level.
LikeLike
The conditions for re-admittance into the Union faced the most backlash from white southerners. The Reconstruction Act of 1867 required former Confederate states to revise their constitution so it gave manhood suffrage. This would include the now freed blacks to have a constitutionally protected right to vote. Southerners resisted in every way possible even go as far as to not vote. The best argument white southerners gave was their opposition to the tax reforms because it was used to fund programs specifically for freedmen. However, this situation wouldn’t have happened if not for the discrimination of white southerners.
LikeLike
Lou Williams’ text on reconstruction revealed how the whites in South Carolina resisted the Republican dominated government that was set up during Reconstruction. As South Carolina prepared to elect and set up their new state government, many white South Carolinians wanted to protest the political process that made black people their political equals. Many of these white South Carolinians had no choice as they were banned from participating, since they served under a Confederate government. Furthermore, the white South Carolinians opposed the Republican government on the basis that they were corrupt and opportunist. These carpet baggers and pickpockets came from the North to control South Carolinian politics. On the issue of taxes, the white population criticized the Republican government for disguising redistribution in the form of taxes and government programs. They made the argument that the taxes violated lassez faire constitutionalism, which required governments to promote the general welfare rather than serving the interest of certain groups at the expense of others. This argument is probably their weakest one, as interest groups have always held considerable influence in government, especially if they have the funds to lobby. Moreover, the white South Carolinians wanted to control government to oppress the newly freed blacks, which would be violating the principles of lassez faire constitutionalism that they boasted during Reconstruction. The only argument that I can sympathize with is the disdain against carpet baggers, like the governor Robert Scott. If I were a South Carolinian I couldn’t imagine someone from Ohio becoming governor and being able to adequately represent my interest or understand my plight.
LikeLike
Thanks, Pablo – your final point on the “carpetbag” governor is particularly important.
LikeLike
According to Lou Faulkner Williams, the aspects of Reconstruction that elicited most resistance from white southerners was the fact that African Americans would be allowed to vote and emancipation because this meant the loss of property that would work their plantations. This included, Republicans who were committed to helping the newly emancipated African Americans who tried to delay the process by not reporting about them and inciting violence, enacting the Black Codes to prevent African Americans from exercising their voting rights. Southerners argued that the new changes created an illegitimate government with Republican leaders and being deprived of their rights for participating in the Civil War in which they stated that this government was consumed with violence, fraud, and military power. They also argued about taxation without representation when their property was taxed while some did not have to pay. The opponents had their best arguments by arguing that this government was illegitimate by forcing Southerners to accept the new conditions in order to be admitted back to the Union and implementing Republican government in the South which destroyed the idea of consent of the governed. However, the worst argument was the fact that Southerners believed that the African Americans needed someone to guide them because they were uncivilized so exercising political and social rights was a threat to the South.
LikeLike
According to Lou Faulkner Williams, despite claiming the freedom from their Masters, the freed slaves were still not free. There were many ways the Southern White population believed that the freed slaves should remain inferior to their race. First, the Black Code of 1865 was enacted by South Carolina which was intended to limit the freedman to pursue any occupation other than farmer or servant and had to obtain a license and pay a ” special tax”. This demonstrates that the white southerners were not accepting the fact that the slaves are free. The belief that the newly freed man is uncivilized and therefore they should be controlled. The black men wanted to be treated equally. They wanted education, participate in political matters and take just live everyday life without being discriminated against. The whites feared because most of the population of the south was black. The Reconstruction Act of 1867 was passed with the intention of readmitting Southern states into the union. The white southerners were resistant to this act because the blacks will be able to vote and become a citizen through the 14th Amendment and the 15th Amendment. Opponents had their best argument when it comes to organizing a whole new South. After the civil war, the South was in debt. For them, they saw it as being disorganized. For example, you have the freed slaves who are not educated enough to know how to build themselves a new life. The worst argument would be not providing citizenship and the right to vote as it is granted in the Amendments. Regardless of their situation, they are granted these rights.
LikeLike
According to Lou Faulkner Williams, despite claiming the freedom from their Masters, the freed slaves were still not free. There were many ways the Southern White population believed that the freed slaves should remain inferior to their race. First, the Black Code of 1865 was enacted by South Carolina which was intended to limit the freedman to pursue any occupation other than farmer or servant and had to obtain a license and pay a ” special tax”. This demonstrates that the white southerners were not accepting the fact that the slaves are free. The belief that the newly freed man is uncivilized and therefore they should be controlled. The black men wanted to be treated equally. They wanted education, participate in political matters and take just live everyday life without being discriminated against. The whites feared because most of the population of the south was black. The Reconstruction Act of 1867 was passed with the intention of readmitting Southern states into the union. The white southerners were resistant to this act because the blacks will be able to vote and become a citizen through the 14th Amendment and the 15th Amendment. Opponents had their best argument when it comes to organizing a whole new South. After the civil war, the South was in debt. For them, they saw it as being disorganized. For example, you have the freed slaves who are not educated enough to know how to build themselves a new life. The worst argument would be not providing citizenship and the right to vote as it is granted in the Amendments. Regardless of their situation, they are granted these rights.
LikeLike
The aspect that elicit the most resistance from white southerners is the forming of the new constitution of South Carolina. It did not involve former leaders and instead involved the input freed people and Northerners (p.8). The opponents of Reconstruction best arguments were against the Republican tax program because they felt the state government was financially punishing South Carolina after the war and the South lacked financial stability. The whites of South Carolinas felt the tax program was infringing on their rights of, no taxation without representation (p.13). Their worst arguments were the fear of freedman retaliating against former master and a race war. (p.3-4)
-Martin Bueno (PSC212)
LikeLike
During the era of Reconstruction racism was in every aspect of the life of almost every southern white family. Whites on the South were afraid that black would gain the same recognition for their labor as they (whites) do, and therefore destroying blacks was really the main point of their activities. As it says in the reading, “Give the Negro political equality and he will gain social equality.” It was just unacceptable for their minds that black people were people too. However, both races recognized being dependable on each other. Rich whites needed “free labor,” poor whites needed not to be the most inferior class in the society, and black needed work to be able to feed themselves. There was also a fear that black people were violent and would rape white women, whether there are lots of documents that actually the slave owners raped black women. (That’s not from the reading, but just from my history knowledge). However, that is how the extra-legal organization that we read for today was formed. In order not to give black people to live their lives, but to destroy everything they have already gained and to destroy every possibility to gain something in the future.
In my opinion, the best arguments of people who were opposed to Reconstruction was the fact that the government should not intervene, the laissez-faire principle. Truly, one can argue for liberal (not liberal in 2020 sense) market and republican form of government which is set in the COTUS as a legitimate opposition to the Reconstruction. However, the argument against race and that black person in the House or Senate would definitely mean degradation is, in my opinion, absurd and not based on any legitimate facts.
LikeLike
The aspect of reconstruction that elicited the most resistance was incorporating the newly freed black people into society. Many white southerners resisted black people by terrorizing black citizens. White southerners also acted in other means of resistance such as refusing to take in the political process to make black people equal by boycotting polls. Black codes were also established in the South which would restrict Black people’s freedom. The economic aspect for white Southerners is where the argument is the strongest because the average income did decrease for white southerners during reconstruction but the argument is still weak because they never paid for labor in the first place during slavery. Williams talks about the Republican program being unacceptable in South Carolina. The Whites claimed to have political frustration, racial antagonism. This is the weakest part of the white southerner’s argument because Black codes and political protest helped the white southerners gain more power in the South and gave less power and rights to black citizens.
LikeLike
Reconstruction was a period after the Civil War when Black slaves were emancipated. Reconstruction was meant to help the succeeded southern states re-enter the union and comply with the laws enacted regarding the emancipation of black people. White Southerners were not happy with the fact that black people were free. According to Williams, the only reason why they surrendered during the civil war and re-entered the union was because they were defeated. White Southerners were especially resistant about black men having the right to vote and participate in government. A lot of white southerners believed that black men were too inferior to participate in government.
One of the best arguments that opponents of reconstruction made was that slavery protected blacks from being harmed by the outside world. They made the argument that when blacks were slaves, they could be protected by their slave masters since they were their property. However, n that blacks are free, anyone could injure them for no reason. The worst argument opponents of slavery made to oppose reconstruction is that freedmen would rise up and have an insurrection against white men. The southern states were filled with a lot of black people due to slavery. During reconstruction, whites feared that blacks would rebel and start a war against them. I think this is the worst argument because black people were not looking to start a war, they had just been freed and the only thing they wanted was to have equal rights as white people and be treated like citizens. Freed black people were excited to finally have the chance to send their kids to school, have their marriages validated under the law, and participate in government. They had no interest in starting a war against white people. They just wanted to be free.
LikeLike
An aspect of Reconstruction that elicited most resistance from white southerners was the emancipation of former slaves. The beginning of the text explains how white southerners “responded to the end of slavery with Black Codes calculated to restrict the liberties of the black population”. The Black Code of 1865 limited the freedom of the recently emancipated slave. ” No black could aspire to any occupation other than a farmer or servant without obtaining a licence and paying a special tax…. patrol laws were re instituted…. blacks are required to make contracts, work from sunup to sundown…”. These codes demonstrated the assumptions that white southerners believed blacks were inferior to whites.
White southerners also responded with violence. “Night riders would terrorized black citizens almost nightly over a period of several months in 1870 and 1871, forcing the freeman to sleep in the woods and swamps for fear of their lives”.
Another aspect of Reconstruction that elicited most resistance from white southerners was the Reconstruction Act of 1867, this act would provide for manhood suffrage, the ratification of the Fourteenth Amendment that provided emancipated slaves national citizenship, the ratification of the Fifteenth Amendment which granted black men the right to vote. The act also laid out the process of readmission of southern states into the Union. White southerners argument was that they “refused to take part in a political process on an equal basis with their former slaves”.
“High property taxes, the primary source of state revenue in Reconstruction South Carolina, enraged the whites who already considered the state government illegal”. White southern Carolinian’s argument against the taxes was the belief that it was taxation without representation.
LikeLike
The white southerners resisted reconstruction through the language in which the amendments were interpreted by judges. They began to oppose it through violence, and fear to reduce freed black slave’s political rights. African Americans now had a voice but, white southern were willing to take it away from them at any cost.
The Ku Klux Klan intimidated the African American’s to keep them from voting, and even killed Republican leaders.
During this time, the privileges and immunities clause was being argued, as well as the interpretation for the 14th amendment. The equal protection was not granted to African American, as the challengers argued the founding father’s interpretation did not guarantee such idea.
The slaughterhouse cases of 1873 was addressed by the judges before they addressed the discriminatory acts African Americans were facing. A monopoly in slaughtering was established in New Orleans and John Campbell used the reconstruction Amendments to his defense. He claimed that the reconstruction amendment did not state equal protection based on race instead anyone can use this amendment to their defense of equal protection of privileges and immunities. In the end Justice Samuel Miller ruled that the purpose of the 14th amendment was to provide citizenship for American Americans. He also distinguished a state citizenship from national citizenship of rights. Many opposed this and argued that the 14th amendment altered the federal system. The privileges of citizenship were a part of their political inheritance as Bradley stated.
LikeLike
According to Lou Faulkner Williams, there was a strong tradition of white supremacy, dual federalism and laissez-faire constitutional principles in which the Republican government failed to secure strong constitutional doctrines and a national rule of law in South Carolina. Some aspects of Reconstruction that evoked most resistance from white southerns was the Republican Congress enforcing the emancipation of proclamation. There is this proslavery rhetoric among the white southerners that since the masters cared and treated for their slaves, and the slaves were “happy,” then there was no reason for the slaves to be freed. White Southerns also wanted to go back to the time before the Civil War, in which the white man was superior than the black man and to keep their control on them. Some white southerns feared of slave insurrection and others believed they had to “help” the freedman since the freedman “lacked the capacity” to be “civilized.” They did this by passing the Black Codes in 1865s, which were meant to limit the “freedoms” a black man could potentially have. White southerners did not want to give equal rights to Black people because of this backward thinking, despite the fact that both the white and black Southerns needed each other to rebuild what was just destroyed.
LikeLike
According to Lou Faulkner Williams, the aspects of Reconstruction in which the white southerners opposed was the mere fact that they did not want to adopt the ideals of the North. The white southerners feared a “Black Republican” state government and despised the idea of Blacks being freedmen, equals. Much of their hatred was being directed towards the carpetbaggers and scalawags, who exploited the South in the time of reconstruction. In a sense, both parties of people executed an early form of gentrification on a macro level, throughout the South, Republican ideals being evangelized and modernizing the life of aristocratic planters. The South had its best arguments in opposition to Reconstruction in terms of being stubborn and not adopting Northern ideals. Southern whites were vulnerable in the process of adjusting to a slavery-free labor force, and would no back down against the North and the now freed Blacks. The worst argument for the Southern whites was presenting the “Ku Klux Klan as the white solution.” The hardheaded mentality of the South could not accept the fact that Blacks were now equaled, thus resorting in treating Blacks as inferiors in order to reinforce the dominance they once had when slavery existed
LikeLike
White southerners mostly resisted their way of life becoming transformed in a way they didn’t approve of. They felt threatened that blacks would become the conquerers and have them become slaves. The fear that depletion of their wealth would happen. The white southerners loathed the federal government telling them how to run their state. They wanted to keep slavery. They even went so far as declaring the constitution illegitimate, causing a rise in dual federalism within their state. They made the argument that slavery would hurt their state economically and threatening their property rights Even though there was a sharecroppers system whereby, whites would allow blacks to produce commodities on their land but had to pay the landowners a share of the crops. Whites opposed blacks being granted land by the state. The white southerners did. everything they could to prevent blacks from advancing they even enacted black codes. The black codes were a wide range of laws restricting blacks from interracial marriages to loitering in a public place. After the Reconstruction Amendments, the Enforcement Act of 1870, and the Klu Klux Klan Act of 1871 the white southerners really resented blacks. The torture and violence against blacks were unspeakable. Yet, in 1883 the Supreme Court overturn acts saying it was up to the states to make such laws, which undermined the Acts.
LikeLiked by 1 person
When the Southern confederates lost to the Republicans in 1865, it wasn’t because they finally agreed to the Republicans political stance but because they were overthrown by their army. Soon after, the republicans began to try and unionize the party promoting democracy and equality for both races, white and black, known as the Reconstruction Era. In order to promote social policies and institutions they increased taxes. They also distributed land amongst the blacks. The Republican party was backed by black votes which had huge influence on its democratic policies.
The conservative white democrats were appalled by this change and sought resistance. They claimed that their constitutional rights were being infringed upon claiming “taxation without representation” and that blacks were a slave race and knew nothing better than being a slave. They claimed that by giving blacks citizenship and representation would give them unwarranted supremacy.
The most convincing argument was taxation with representation because the increased taxes did allow the Republican government to take over their property. Overall their arguments were fueled by racism and hatred towards the ideas that blacks could be treated as equals. Thus, all their arguments were invalid arguments.
LikeLike
The aspects of Reconstruction that elicited the most resistance from white southerners were the amendments that came about it. The 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments ensured black americans freedom from slavery with voting rights granted and citizenship. This ended up with black codes being implemented by white southerners to limit the new freedoms black americans were granted and use them as cheap labor with low pay wages. “White South Carolinians enacted the black codes to reestablish order and perhaps even to protect the former slaves, but the laws demonstrated above all the white southerners fundamental assumption that blacks were inherently, immutably inferior to whites” (Williams, 3). Their worst argument to the Reconstruction era and the amendments that followed after was that ” some white southerners allegedly believed the freedpeople needed protection because they were a race of children who were incapable of reaching a civilized state” (Williams, 3). The former slaves know how the world and society work. They have been enslaved for numerous generations and to think that the white southerners believe that they are a group of childlike people because of their skin is ridiculous. The argument makes no sense and it was just their reasoning to get black americans back under their command since they relied on black labor for everything. I don’t think that the opponent against Reconstruction had any good argument in this text. Most of their arguments were either ‘black americans are too inferior to fend for themselves’ or ‘this would end up in a race war with the black americans rising up against their master’. All of their arguments were extremely racist, ignorant and made no sense at all and were just mostly wild scenarios as to what would happen to them and their economy if they can’t have slavery and former black slaves under their control.
LikeLike
Southern whites resisted efforts of reconstruction after the Civil War because they had been forced into a corner to accept the Reconstruction Act of 1867 as a condition to re-enter the Union. They refused to participate alongside legislators or voters and boycotted what they saw an illegitimate state legislature. The aspect that most angered them was that new social policies favored the rights and promoted the well being of black people over what they saw as the general welfare in the state. When property taxes led to their land being confiscated and redistributed to others they argued that their constitutional rights were being jeopardised. The land owning and educated elite had entitled themselves as the only qualified individuals to govern and tax the illiterate, unencumbered and each other in the states, so when the those public offices were given to out of state appointees and landless people of color they felt disenfranchised.. They contended that they were not represented in government and being taxed without representation.
I think southerners who felt that their government was illegitimate were not wrong. Outside appointee came in and punished them and profited off their stations. But the south’s refusal to participate in post war government pride lead to a perpetuating this. The sticker shock social services with out the head tax on slaves, is just a result of centuries of elitist conditioning.
LikeLike